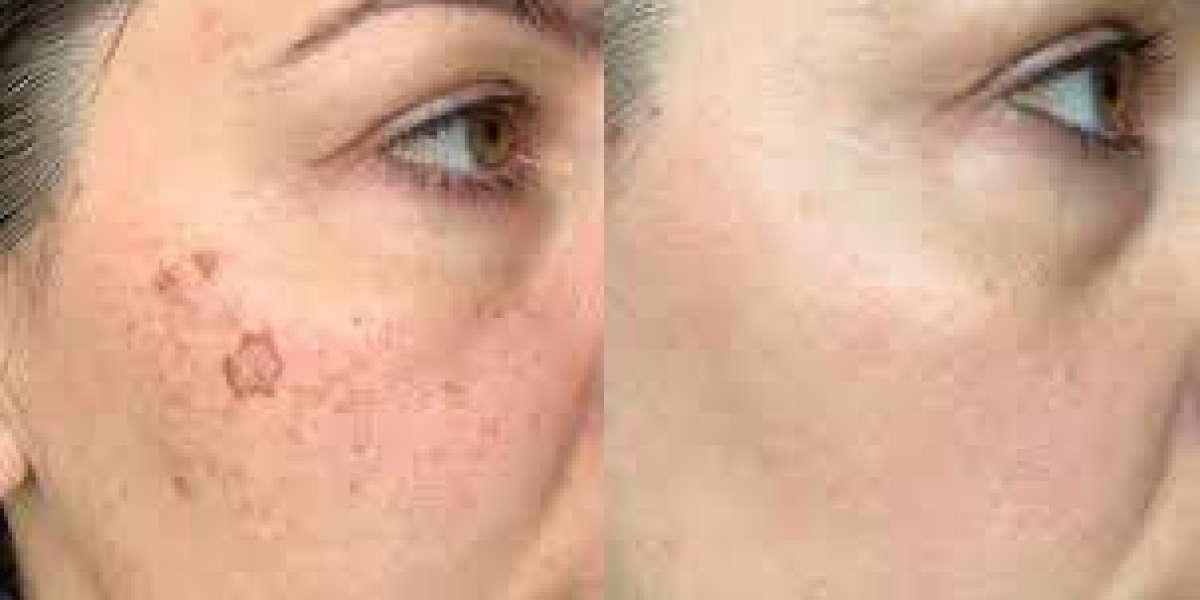
Pigmentation treatment encompasses a variety of approaches aimed at addressing skin discoloration, uneven tone, and dark spots. Whether caused by sun exposure, hormonal changes, or skin injuries, pigmentation issues can impact self-esteem and overall skin health. Understanding the available treatment options, their mechanisms, and considerations is crucial for effective management. Here's what you need to know about pigmentation treatment:
Types of Pigmentation:
- Hyperpigmentation: Darkened patches or spots caused by excess melanin production.
- Hypopigmentation: Lightened patches or spots due to decreased melanin production.
- Melasma: Symmetrical brownish Pigmentation Treatment In Dubai, often associated with hormonal changes.
- Sunspots: Flat, brown spots caused by sun exposure.
- Post-inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): Dark spots resulting from skin inflammation or injury.
Treatment Options:
- Topical Treatments: Creams, serums, and lotions containing ingredients like hydroquinone, retinoids, vitamin C, or kojic acid.
- Procedures: Chemical peels, laser therapy, intense pulsed light (IPL), microdermabrasion, and cryotherapy.
- Prescription Medications: Corticosteroids, tranexamic acid, and tretinoin prescribed by dermatologists.
- Home Remedies: Natural ingredients like lemon juice, aloe vera, or licorice extract may offer mild benefits.
Mechanisms of Treatment:
- Inhibition of Melanin Production: Many treatments work by inhibiting the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color.
- Promotion of Skin Renewal: Some treatments stimulate skin cell turnover, helping to fade pigmentation and reveal fresh, even-toned skin.
- Targeted Destruction of Pigmented Cells: Procedures like laser therapy or chemical peels target and break down excess pigment in the skin.
Considerations:
- Skin Type: Treatment effectiveness and potential side effects can vary based on skin type and sensitivity.
- Treatment Duration: Results may take time, with multiple sessions often required for noticeable improvement.
- Sun Protection: Sunscreen is essential to prevent further pigmentation and protect treated skin from UV damage.
- Consultation: Always consult with a dermatologist or skincare professional to determine the most suitable treatment plan for your specific needs.
Conclusion: Pigmentation treatment offers a range of options for addressing skin discoloration and achieving a more even-toned complexion. By understanding the available treatments, their mechanisms, and considerations, individuals can make informed decisions and work towards clearer, healthier-looking skin. Consulting with a qualified skincare professional is essential for developing a personalized treatment plan tailored to individual needs and concerns.