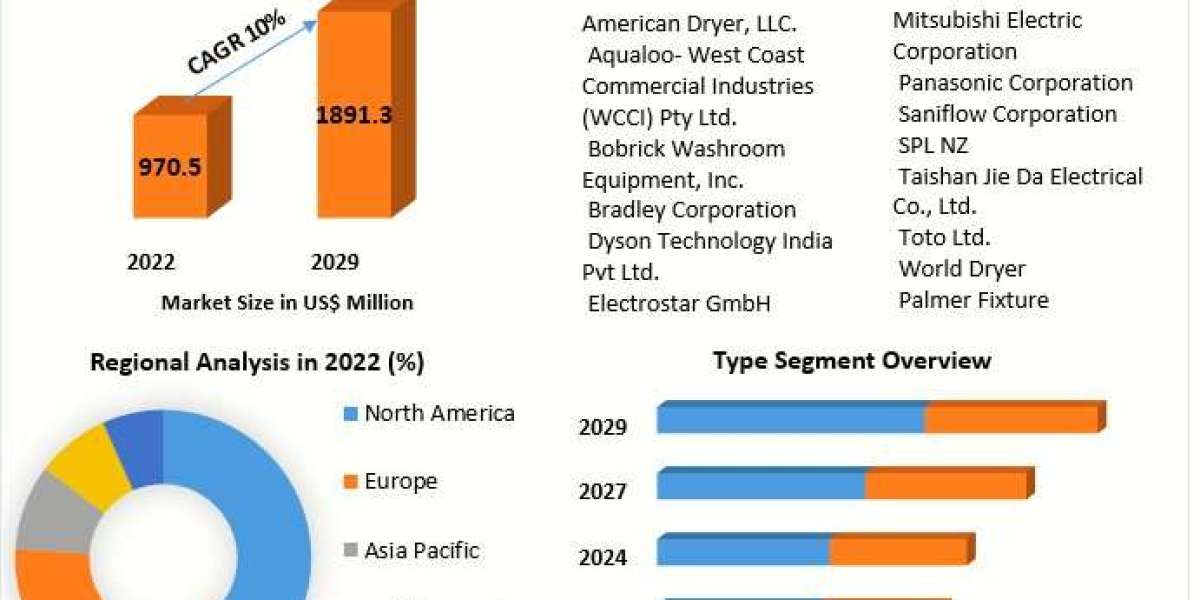
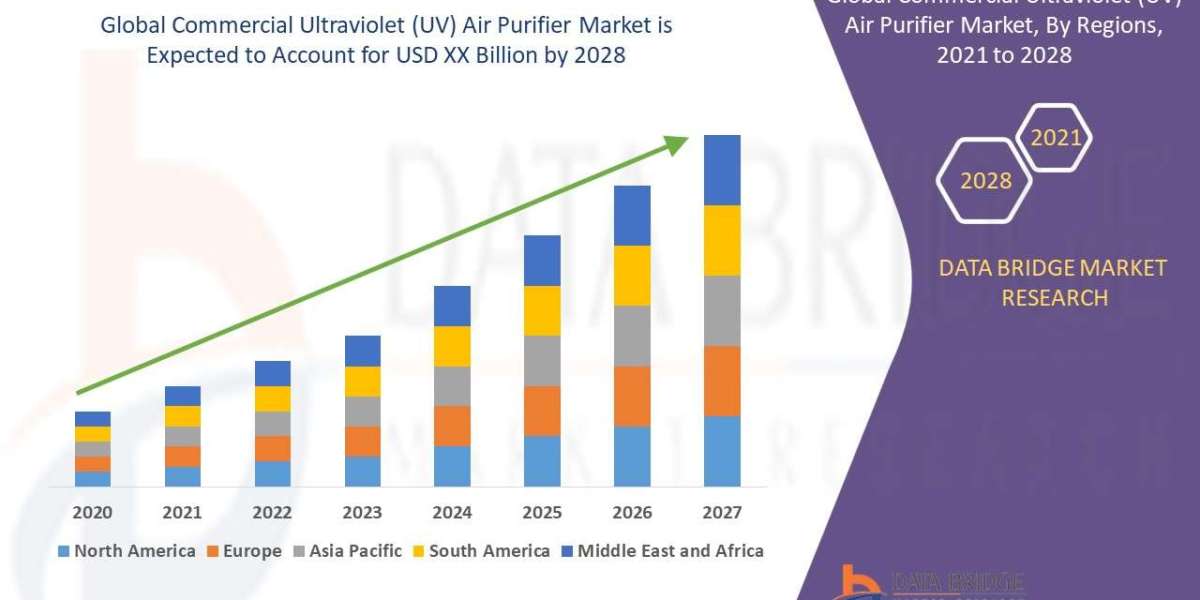
Therapeutic antibody discovery is a complex and dynamic process that requires a multidisciplinary approach, cutting-edge technologies, and innovative methodologies to identify antibodies with the desired pharmacological properties. Nona Biosciences, a leader in the field of biotechnology, adopts a comprehensive strategy for therapeutic antibody discovery, leveraging proprietary platforms, advanced screening methodologies, and collaborative partnerships to accelerate the identification and development of novel therapeutic antibodies.
Central to Nona Biosciences' approach to therapeutic antibody discovery is its proprietary Harbour Mice® platform, a groundbreaking technology that enables the generation of fully human monoclonal antibodies with exceptional specificity and affinity. Unlike traditional methods that rely on immunization with foreign antigens, Harbour Mice® leverages genetically engineered mice capable of producing fully human antibodies, offering unparalleled control over the antibody discovery process. This innovative platform allows researchers at Nona Biosciences to rapidly generate lead antibody candidates with the desired pharmacological properties, paving the way for the development of next-generation therapeutics.
In addition to its Harbour Mice® platform, Nona Biosciences employs a variety of advanced screening methodologies to identify antibodies with the desired therapeutic potential. One such methodology is the use of high-throughput screening assays, which enable researchers to assess the binding affinity, specificity, and functional activity of candidate antibodies against their intended targets. These assays, which may include enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA), surface plasmon resonance (SPR), and cell-based assays, provide valuable insights into the biological activity of antibodies and their potential efficacy as therapeutic agents.
Furthermore, Nona Biosciences harnesses the power of advanced computational methods and artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of therapeutic antibody discovery. By leveraging AI-driven algorithms, predictive modeling, and data analytics, Nona Biosciences can analyze vast amounts of biological data to identify promising antibody candidates, predict their pharmacological properties, and optimize their therapeutic potential. This data-driven approach accelerates the antibody discovery process, reduces the time and resources required for candidate selection, and increases the likelihood of success in clinical development.
Collaboration lies at the heart of Nona Biosciences' approach to therapeutic antibody discovery, with the company actively partnering with academic institutions, research organizations, and biotechnology companies to leverage collective expertise and resources. Through strategic collaborations, Nona Biosciences gains access to cutting-edge technologies, novel biological targets, and specialized expertise, accelerating the translation of scientific discoveries into tangible therapeutic outcomes. By fostering a collaborative ecosystem of innovation, Nona Biosciences expands the scope of its antibody discovery efforts and maximizes the potential impact of its research on patient care and public health.
In summary, Nona Biosciences adopts a comprehensive and innovative approach to therapeutic antibody discovery, leveraging proprietary platforms, advanced screening methodologies, computational biology, and collaborative partnerships to accelerate the identification and development of novel therapeutic antibodies. By combining scientific excellence with a commitment to innovation and collaboration, Nona Biosciences is advancing the field of biotechnology and paving the way for the development of next-generation therapeutics that address unmet medical needs and improve patient outcomes.