Enlarged prostate cancer, a condition that affects millions of men worldwide, is often surrounded by confusion and misinformation. One common misconception is that it's possible to detect enlarged prostate cancer without conducting any tests. In this blog, we'll debunk this myth and shed light on the importance of proper diagnosis and testing for detecting prostate cancer.
Understanding Enlarged Prostate Cancer
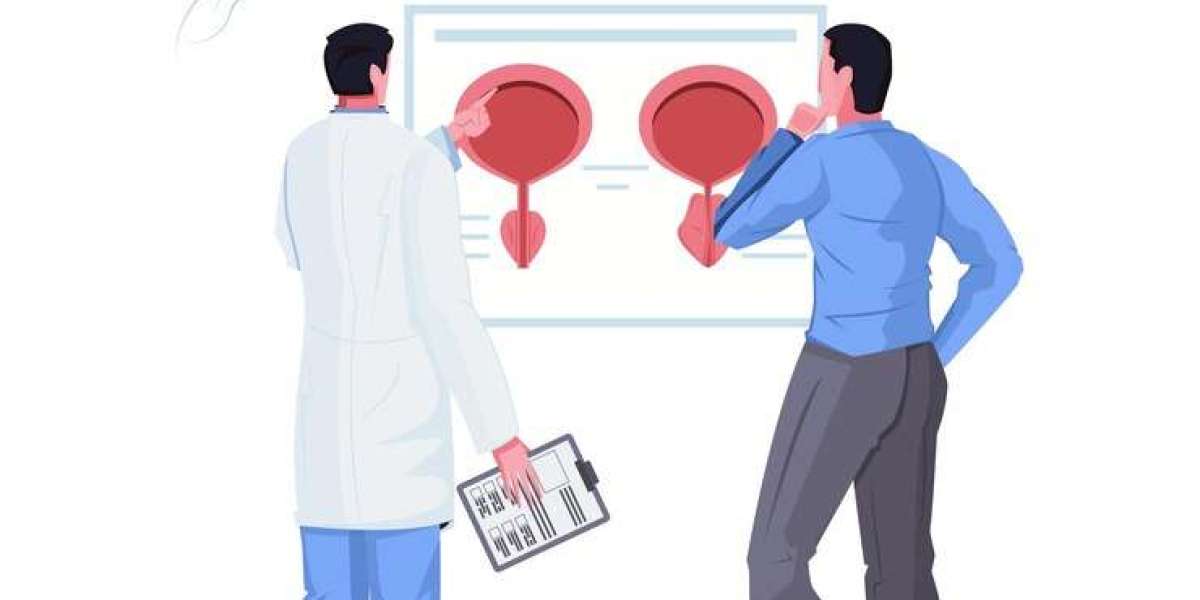
Enlarged prostate cancer, also known as prostate adenocarcinoma, occurs when cancerous cells develop within the prostate gland. It's essential to distinguish between an enlarged prostate due to benign causes, such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), and an enlarged prostate due to cancerous growth.
Debunking the Myth
Contrary to popular belief, it is not possible to definitively diagnose enlarged prostate cancer without conducting specific tests. While symptoms suggestive of prostate issues, such as frequent urination, difficulty urinating, weak urine stream, or urinary urgency, may raise suspicion, they are not exclusive to prostate cancer. These symptoms can also be attributed to benign conditions like BPH.
The Importance of Testing
To accurately diagnose prostate cancer or determine if an enlarged prostate is due to cancerous growth, various tests are typically conducted:
Digital Rectal Examination (DRE): A doctor inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum to feel the prostate gland and assess its size, shape, and any abnormalities. While DRE provides valuable information, it cannot definitively diagnose prostate cancer on its own.
Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test: This blood test measures the levels of PSA, a protein produced by the prostate gland. Elevated PSA levels can indicate potential prostate issues, including prostate cancer. However, PSA levels can also be elevated due to other factors, such as BPH or inflammation.
Imaging Studies: Imaging tests like transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be used to visualize the prostate gland and detect abnormalities. These tests can help guide further diagnostic procedures, such as biopsies.
Prostate Biopsy: A biopsy involves taking small tissue samples from the prostate gland using a needle guided by ultrasound. The tissue samples are then examined under a microscope to detect the presence of cancerous cells. Biopsy is the gold standard for diagnosing prostate cancer.
Conclusion
While experiencing symptoms suggestive of prostate issues may prompt concerns about prostate cancer, it's important to recognize that proper diagnosis requires specific tests. Relying solely on symptoms or physical examination is not sufficient for diagnosing prostate cancer accurately. If you or someone you know experiences symptoms suggestive of prostate issues, it's crucial to consult a healthcare professional for appropriate evaluation and testing. Early detection and timely intervention can significantly impact treatment outcomes and overall prognosis for prostate cancer.