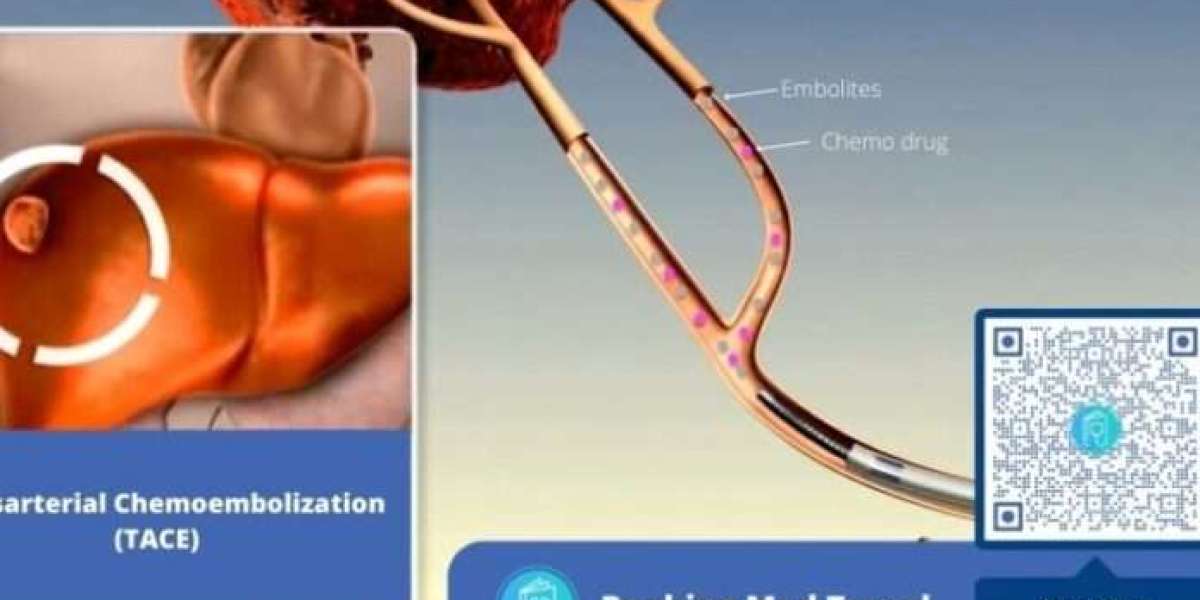
Facing liver cancer can be overwhelming, and treatment options like the TACE procedure might leave you with questions. Let’s delve into the world of TACE, exploring its success rates, suitability, types, benefits, steps involved, and answers to frequently asked questions—all in straightforward language.
Why Choose TACE?
TACE shines in specific liver cancer scenarios:
Unrespectable tumors: When surgery isn’t possible due to tumor size, location, or underlying health conditions, TACE offers a minimally invasive alternative.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): This most common type of primary liver cancer often responds well to TACE.
Intermediate-stage HCC: TACE proves effective in managing tumor growth and prolonging survival in this stage.
HCC following surgery or other treatments: TACE can combat recurrent tumors or prevent their development.
TACE Types Tailored to Your Needs
Conventional TACE: This standard approach delivers chemotherapy drugs directly to the tumor via a catheter inserted into an artery.
Drug-eluting bead TACE (DEB-TACE): Tiny beads loaded with medication are used, potentially offering sustained drug release and improved tumor targeting.
Yttrium-90 radioembolization (Y-90 TACE): Radioactive beads emit radiation within the tumor, maximizing local effectiveness.
Benefits of the TACE Procedure
Targeted therapy: Chemotherapy reaches the tumor directly, minimizing harm to healthy liver tissue.
Tumor control: Studies show TACE can shrink or stabilize tumors in approximately 60-70% of cases.
Improved survival: TACE can significantly improve life expectancy, especially in intermediate-stage HCC.
Fewer side effects: Compared to systemic chemotherapy, TACE often causes milder side effects.
Minimally invasive: The procedure involves tiny incisions and shorter hospital stays.
The TACE Procedure: A Step-by-Step Guide
Preparation: You’ll undergo imaging tests, blood work, and consultations to ensure TACE is right for you.
Catheterization: A thin, flexible tube (catheter) is inserted into an artery in your groin and guided to the liver.
Embolization: Tiny particles—often mixed with chemotherapy drugs—are released to block blood flow to the tumor.
Monitoring and Recovery: You’ll be monitored for a few hours, and most patients go home the same day or the next. You may experience pain, fatigue, nausea, or fever, which usually subside within a week.
Understanding the Success Rates of TACE
Success rates for TACE vary depending on individual factors like:
Tumor type and stage: Early-stage HCC generally responds better than advanced stages.
Liver function: Good liver health increases the likelihood of success.
Overall health: Other medical conditions can influence outcomes.
While definitive success rates depend on these factors, here’s what research suggests:
Tumor control: TACE can stop tumor growth or shrink tumors in 60-70% of cases.
Survival: Studies show TACE can improve median survival by 12-18 months compared to no treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about TACE
Is TACE painful?
The procedure itself is typically done under local anesthesia, so you shouldn’t feel pain. You may experience discomfort or pain afterward, which medications can help manage.
Are there side effects?
Common side effects include fatigue, nausea, fever, abdominal pain, and loss of appetite. These usually subside within a week. Inform your doctor if any side effects are severe or persistent.
What are the risks of TACE?
Risks include allergic reactions to medication, bleeding, infection, and liver damage. Your doctor will discuss these risks in detail before the procedure.
What happens after TACE?
You’ll likely have follow-up imaging tests to monitor your tumor response and overall health. Your doctor will recommend further treatment options based on your individual needs.
How much does TACE cost?
Costs vary depending on your insurance coverage, hospital fees, and other factors. Talk to your insurance provider and discuss cost estimates with your healthcare team.
Is TACE a cure?
No, TACE is primarily used to control tumor growth and improve symptoms, not as a definitive cure.
What are the side effects of TACE?
Common side effects include pain, nausea, fatigue, fever, and abdominal discomfort. These are usually temporary and manageable.
What are the risks of TACE?
Serious risks are uncommon, but can include liver damage, infection, and bleeding.
Who is a good candidate for TACE?Talk to your doctor to see if TACE is right for you based on your individual circumstances.
What happens after TACE?
You’ll likely have follow-up imaging tests to monitor your tumor response and overall health. Your doctor will recommend further treatment options based on your individual needs.