In the United States, the regulatory landscape for aesthetic implant procedures is governed by various federal regulations, guidelines, and oversight bodies aimed at ensuring patient safety, product efficacy, and regulatory compliance.
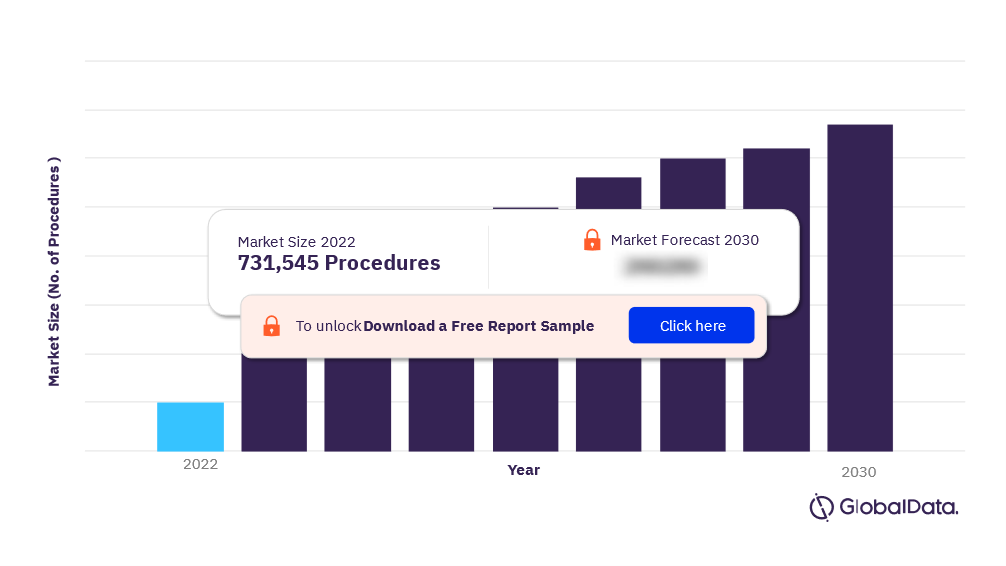
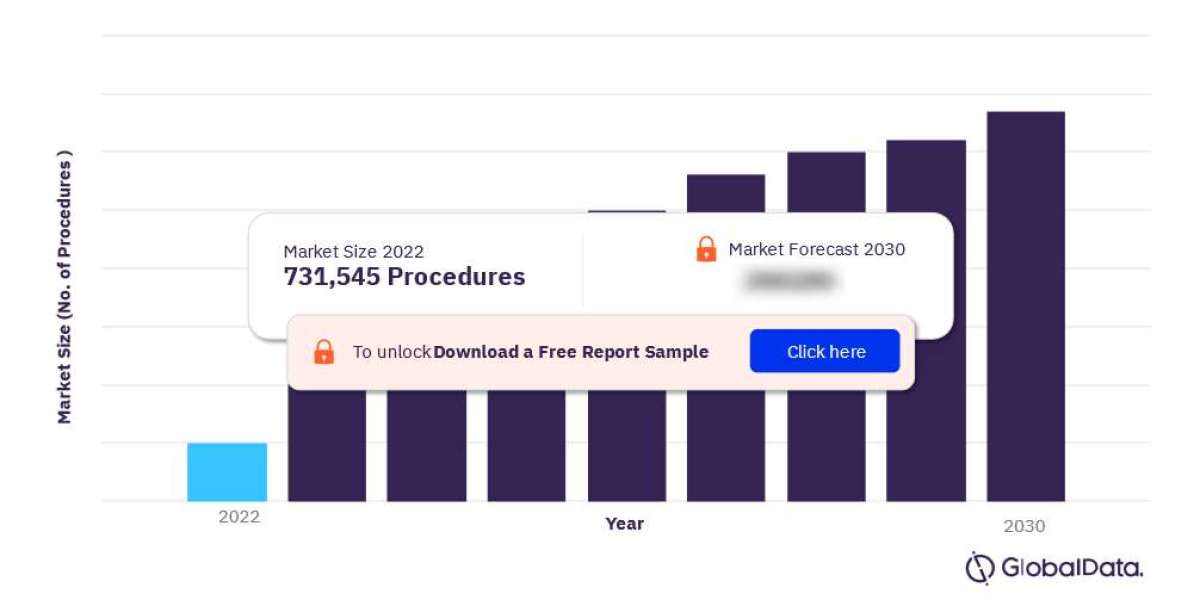
For more insights on the US Aesthetic Implant procedures market forecast, download a free report sample
Here's an overview of the regulatory landscape, compliance requirements, and standards applicable to the US aesthetic implant procedures market:
Food and Drug Administration (FDA): The FDA is the primary regulatory authority responsible for overseeing medical devices, including aesthetic implants, in the United States. Aesthetic implants are classified as Class II or Class III medical devices, depending on their intended use and associated risks.
Premarket Approval (PMA): Class III aesthetic implants require FDA premarket approval through the PMA process. Manufacturers must submit comprehensive scientific data, including clinical evidence, demonstrating the safety and efficacy of the implant for its intended use.
Premarket Notification (510(k)): Most Class II aesthetic implants are subject to the 510(k) premarket notification process, whereby manufacturers demonstrate substantial equivalence to a legally marketed predicate device. The FDA evaluates whether the new device is as safe and effective as the predicate device.
Quality System Regulation (QSR): The FDA's Quality System Regulation (21 CFR Part 820) sets forth requirements for the design, manufacture, packaging, labeling, storage, and distribution of medical devices, including aesthetic implants. Manufacturers must establish and maintain a quality management system that complies with QSR requirements to ensure the safety and effectiveness of their products.
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP): Aesthetic implant manufacturers are required to adhere to GMP standards outlined in the Quality System Regulation. GMP encompasses manufacturing processes, quality control measures, facility design, equipment calibration, personnel training, and documentation practices to ensure consistent product quality and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Post-Market Surveillance (PMS) and Reporting: Manufacturers are required to establish post-market surveillance systems to monitor the safety and performance of aesthetic implants following their commercialization. This includes collecting and analyzing adverse event reports, conducting post-market studies, and implementing corrective actions or recalls when necessary. Manufacturers must also report adverse events and product malfunctions to the FDA as required by regulations.
Labeling and Advertising Regulations: Aesthetic implant labeling and advertising must comply with FDA regulations governing the promotion of medical devices. Labeling must include essential information such as indications for use, contraindications, warnings, precautions, adverse reactions, and instructions for use. Advertising materials must be truthful, not misleading, and substantiated by scientific evidence.
Clinical Trials and Evidence Requirements: For Class III aesthetic implants requiring premarket approval, manufacturers must conduct clinical studies to generate sufficient clinical evidence supporting the safety and efficacy of the device for its intended use. Clinical trial design, conduct, and reporting must comply with FDA regulations and guidance documents outlining best practices for clinical research.
International Standards and Harmonization: Aesthetic implant manufacturers may also reference international standards and harmonization efforts to demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements. Standards such as ISO 13485 (Quality Management Systems for Medical Devices) and ISO 14971 (Risk Management for Medical Devices) provide frameworks for ensuring product quality, safety, and regulatory compliance.
Overall, compliance with FDA regulations, quality standards, and post-market surveillance requirements is essential for manufacturers of aesthetic implants to ensure patient safety, product quality, and regulatory compliance throughout the product lifecycle. By adhering to these regulations and standards, manufacturers can demonstrate the safety and efficacy of their products and maintain public trust in the aesthetic implant procedures market.