Dental implants represent a transformative solution for individuals seeking to restore their smiles, functionality, and confidence. In the United Kingdom, dental implants have become increasingly popular as a long-term option for replacing missing teeth and improving oral health. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of dental implants in the UK, including their benefits, procedures, considerations, and advancements in implant dentistry.
Understanding Dental Implants
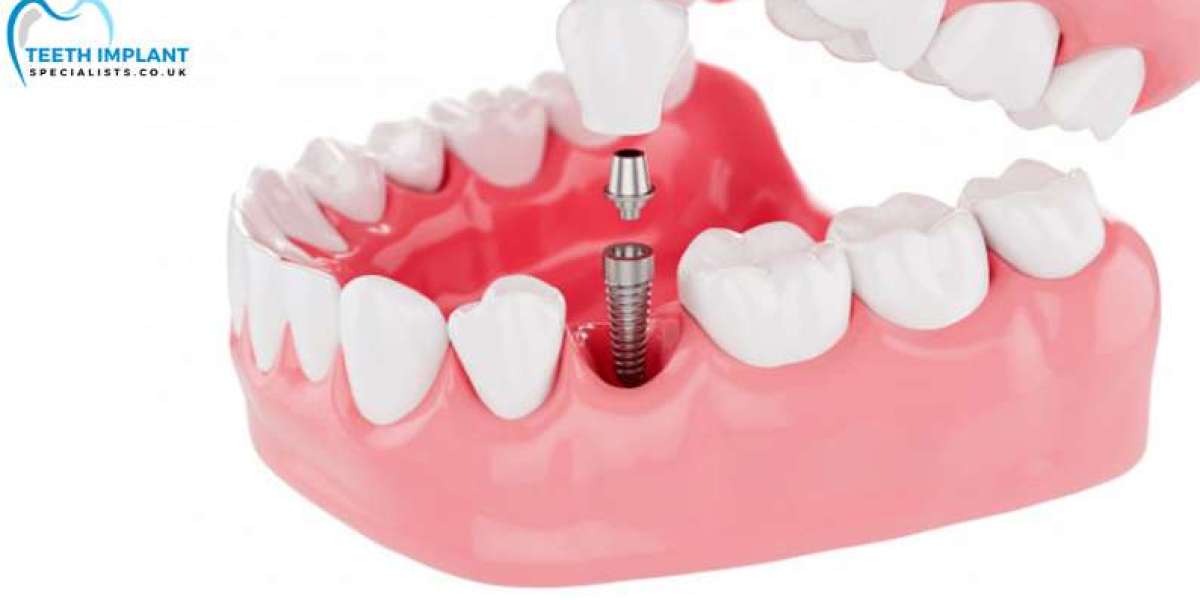
Dental implants are prosthetic tooth roots made of biocompatible materials, such as titanium, that are surgically placed into the jawbone to support replacement teeth or dental prostheses. They serve as a sturdy foundation for crowns, bridges, or dentures, mimicking the natural structure and function of teeth. Dental implants offer numerous advantages over traditional tooth replacement options, including improved stability, durability, and aesthetics.
Types of Dental Implants
Endosteal Implants:
Endosteal implants are the most common type of dental implants used in the UK. They are surgically placed directly into the jawbone and serve as anchors for individual crowns, bridges, or dentures. Endosteal implants offer excellent stability and long-term reliability, making them a preferred choice for many patients.
Subperiosteal Implants:
Subperiosteal implants are placed on top of the jawbone, beneath the gum tissue. They are suitable for patients who have insufficient bone density or height to support traditional endosteal implants. Subperiosteal implants consist of a metal framework that rests on the jawbone and supports the replacement teeth. While less common than endosteal implants, subperiosteal implants offer a viable alternative for certain individuals.
Dental Implant Procedures
The process of receiving dental implants typically involves the following stages:
Initial Consultation:
The journey begins with an initial consultation with a qualified implant dentist. During this visit, the dentist evaluates the patient's oral health, discusses treatment goals and expectations, and performs diagnostic tests, such as X-rays and impressions, to assess bone density and structure.
Treatment Planning:
Based on the results of the initial assessment, the dentist develops a personalized treatment plan tailored to the patient's unique needs and preferences. This plan outlines the number of implants required, the type of restoration (crown, bridge, or denture), and the timeline for treatment.
Implant Placement:
The next step involves the surgical placement of the dental implants into the jawbone. This procedure is performed under local anesthesia or sedation to ensure patient comfort. Using specialized instruments and techniques, the dentist carefully creates small incisions in the gums, prepares the implant sites, and inserts the implants into the jawbone.
Osseointegration:
Following implant placement, a process called osseointegration occurs, during which the implants fuse with the surrounding bone tissue. This integration process typically takes several months, during which the implants become firmly anchored in the jawbone, providing a stable foundation for the prosthetic teeth.
Restoration:
Once osseointegration is complete, the final restoration can be attached to the dental implants. This may involve the placement of individual crowns, implant-supported bridges, or implant-retained dentures, depending on the patient's treatment plan and aesthetic preferences.
Considerations for Patients
Oral Health and Bone Density:
Good oral health and adequate bone density are essential prerequisites for successful dental implant treatment. Patients with underlying dental issues, such as gum disease or insufficient bone volume, may require additional procedures, such as bone grafting or periodontal therapy, to prepare for implant placement.
Patient Candidacy:
Not all individuals are suitable candidates for dental implants. Factors such as overall health, smoking habits, and medical history may influence eligibility for treatment. Patients are encouraged to undergo a thorough evaluation and consultation with an experienced implant dentist to determine candidacy and explore alternative treatment options if necessary.
Maintenance and Care:
Proper maintenance and care are critical for preserving the longevity and success of dental implants. Patients should adhere to a diligent oral hygiene routine, including brushing, flossing, and regular dental check-ups, to prevent complications such as peri-implantitis (inflammation of the gum tissue around implants) and implant failure.
Long-Term Investment:
While dental implants represent a significant investment in terms of time and resources, they offer long-term benefits and improved quality of life for patients. The durability, functionality, and aesthetics of dental implants make them a worthwhile investment for restoring oral health and confidence.
Advancements in Implant Dentistry
Advancements in technology and techniques have revolutionized the field of implant dentistry, enhancing precision, efficiency, and patient outcomes. Some notable advancements include:
Computer-Aided Design and Manufacturing (CAD/CAM) Technology:
CAD/CAM technology enables dentists to design and fabricate custom-made implant restorations with unparalleled accuracy and precision. This technology streamlines the treatment process and ensures optimal fit, function, and aesthetics for patients.
Guided Implant Surgery:
Guided implant surgery utilizes advanced imaging and computer-guided navigation systems to plan and execute implant placement with pinpoint accuracy. This minimally invasive approach reduces surgical trauma, shortens recovery times, and enhances overall treatment predictability.
Biomaterials and Surface Modifications:
Ongoing research and development in biomaterials and surface modifications have led to the introduction of implant materials with enhanced biocompatibility, osseointegration, and soft tissue response. These innovations contribute to improved long-term success rates and patient satisfaction with dental implants.
Conclusion
Dental implants represent a groundbreaking solution for restoring missing teeth and rejuvenating smiles in the UK and beyond. With their remarkable stability, functionality, and aesthetics, dental implants offer a transformative treatment option for individuals seeking to regain confidence and oral health. By understanding the types of implants available, the treatment process, important considerations for patients, and recent advancements in implant dentistry, individuals can make informed decisions about their oral health and embark on a journey towards a brighter, more vibrant smile.